Content
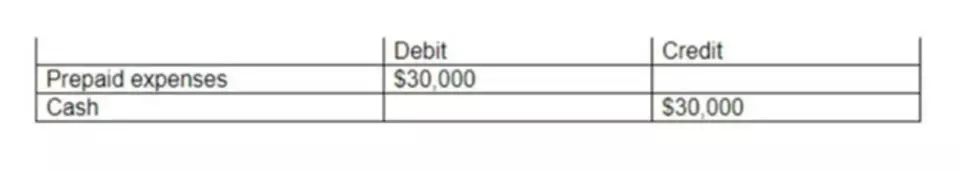
Identify and explain two liability categories on the classified balance sheet, and give examples of each category. Differentiate between a current liability and a long-term liability. Distinguish between a contingent liability and an actual liability and give three examples https://www.bookstime.com/ of each. Describe what accounts are considered liability and asset accounts. If the business has more than one checking account, for example, the chart of accounts might include an account for each of them. A small business owner must not eliminate all liabilities.
Juventus Lays Bare Soccer’s Rotten Finances – The Washington Post
Juventus Lays Bare Soccer’s Rotten Finances.
Posted: Tue, 29 Nov 2022 20:24:23 GMT [source]
A larger company likely incurs a wider variety of debts while a smaller business has fewer liabilities. Contingent liabilities are only recorded on your balance sheet if they are likely to occur. Here is a list of current and non-current liabilities. They arise from purchase of inventory to be sold, purchase of office supplies and other assets, use of electricity, labor from employees, etc. Provide an example of how debits and credits impact accounts.
Disadvantages of Liabilities
Hat proportion of the company’s total funding is provided by creditors? The total debt to assets ratio metric addresses this question. This metric compares two Balance sheet entries, total liabilities (i.e., total debt) and liability accounts total assets. Second, balance sheet debt also appears under Long-term liabilities such as 5-year, 10-year, or longer term notes or bonds sold to the public. Liabilities finance your business and pay for large expenditures.
- Right now it’s important just to know the basic concepts.
- Related items could be intangible assets such as patents.
- The accounting equation dictates that when liabilities are paid, the assets of the company decreased by the same amount.
- The liability would continue to be recorded as a non-current liability until its last year of maturity.
Explain why each is considered a contingent liability. There is a trade-off between simplicity and the ability to make historical comparisons. Initially keeping the number of accounts to a minimum has the advantage of making the accounting system simple. Starting with a small number of accounts, as certain accounts acquired significant balances they would be split into smaller, more specific accounts.
Free Accounting Courses
“Accounts payable” refers to an account within the general ledger representing a company’s obligation to pay off a short-term obligations to its creditors or suppliers. AP typically carries the largest balances, as they encompass the day-to-day operations. AP can include services,raw materials, office supplies, or any other categories of products and services where no promissory note is issued.
Which accounts are liabilities?
Recorded on the right side of the balance sheet, liabilities include loans, accounts payable, mortgages, deferred revenues, bonds, warranties, and accrued expenses. Liabilities can be contrasted with assets. Liabilities refer to things that you owe or have borrowed; assets are things that you own or are owed.











